U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
The technical part of the visit to Glasgow included:
The Scottish Executive is the U.S. equivalent of a State DOT. The Scottish Executive receives funding from the U.K. government that includes some earmarks.
For public transport, Traveline is being expanded to Transport Direct for individual information and travel planning services. The nationwide number "0870 608 2608" for Traveline provides information for making local and national journeys. The Scottish Executive funds and operates the call center. Funding is also contributed by transport operators. Transport Direct will be available on the Internet, in kiosks, and on digital television. Purchase of tickets will be available on-line and is funded by DTLR.
For Traveline in Scotland, the cost of a 3-minute call is 24 pence, which is the maximum peak-time rate cost. The "0870" U.K.-wide national rate number system was introduced in January 2001. It is being set up by the Scottish Executive, and operations will be undertaken by a private contractor. The call flow is as follows:
Currently, Traveline receives 7,000 calls per week and can accommodate an expansion of 35 percent. The system is not yet promoted extensively.
The Strathclyde Passenger Transport Executive consists of the City of Glasgow and 12 other council areas. Its duties include developing general passenger policies, reporting to the executive, promoting competition, and providing services for the disabled. Some 44,000,000 rail passengers use 180 stations on 334 route miles per annum. There are 159 subsidized operations for bus services.
Strathclyde Passenger Transport Executive operates the Buchanan Bus Station in downtown Glasgow. It is the largest bus station in Scotland (600,000 buses visit it annually), and it has 57 front-loading bays. The bus service is provided for long distance and express routes. The station provides travel service and information. Electronic passenger information is provided continuously.
 Figure 48. Buchanan Bus Station, Glasgow.
Figure 48. Buchanan Bus Station, Glasgow.
Transportation in Glasgow falls under land services and is one of 11 departments. The population of the city is 620,000, and there are 2.1 million people in the region.

Figure 49. Bus arrival information, Glasgow.
The extensive motorway system has between three and five lanes per direction. The modal split in the city is:
Transportation policy emphasizes parking control and quality public transit services in an effort to mitigate traffic congestion and growth. There is a national policy initiative toward congestion pricing as a means of reducing traffic, but it is not favored in Glasgow. The Glasgow City Council developed a policy approach called the Millennium Plan, which includes:
Historically, traffic has been addressed by ITS implementation, and research has been undertaken to estimate the impact of IT on traffic congestion. The research found that a projected 40 percent increase in traffic can be reduced to 17 percent through telecommuting and other soft means by 2017. Additionally, it has been proved that accident rates are reduced as a result of addressing congestion, environment, and safety.
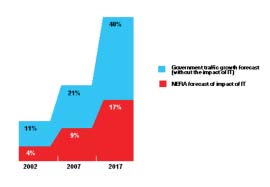 Figure 50. Impact of information technology on traffic flow in Glasgow.
Figure 50. Impact of information technology on traffic flow in Glasgow.
 Figure 51. Message sign in Glasgow.
Figure 51. Message sign in Glasgow.
ITS applications in Glasgow include video, ramp metering, and the NADICS driver information system. It also covers the trunk road network with VMS at key decision points. TrafficMaster, the private-sector traveler information provider, also collects data on the road network. The City of Glasgow also participates in other European projects including OPERA, TABASCO, and ISIS. The NADICS system integrates the national motorway and Glasgow urban highways. ALINIA is the project that researched ramp metering. The signal control is a UTC MOVA SCOOT system. Lane control management is in use in Glasgow through dynamic lane control signs.
The COMPANION hazard warning system provides early warning to motorists. The Journey Enquiry Support System provides point-to-point information for all transportation modes in the Strathclyde region. It provides impartial, point-to-point information and requires a quick response for the 763 routes, 132 bus operators, 1 rail operator, and 3 ferry operators that it serves. The data are captured from bus profiles, 900 stops, and 181 rail stations. At the moment, it is a professional user system and will be expanded to public access at a later stage.
 Figure 52. Variable speed limits in Glasgow.
Figure 52. Variable speed limits in Glasgow.
NADICS covers most of Scotland's main roads. It is divided into six urban areas. It offers integrated control of traffic, management of roads, and is operated in the interest of road safety and network efficiency. The system provides timely and accurate information and is delivered with a user focus. The six urban areas are Glasgow, Stirling, Edinburgh, Dundee, Aberdeen, and Inverness.
 Figure 53. CITRAC and NADICS traffic management center, Glasgow.
Figure 53. CITRAC and NADICS traffic management center, Glasgow.
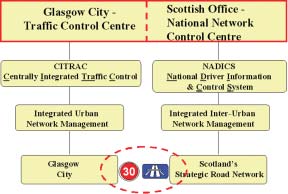 Figure 54. Glasgow CITRAC and Scottish NADICS integration systems.
Figure 54. Glasgow CITRAC and Scottish NADICS integration systems.
The core functions of the systems include:
The NADICS system contains the following parameters:
Typical responses are warnings to drivers, using an algorithmic/planned response sequence (control and information), and dynamic tracking of responses and dynamic removal of the response when completed. The ALINEA ramp metering algorithm is used for ramp metering in Glasgow center. It provides great benefits in capacity improvement and shockwave suppression. Alternate routing and signalizing are provided on city streets when ramp metering and queuing ensues.
The NADICS website is at www.nadics.org.uk. The website was launched in September 2001. CCTV images are provided to the media as well. In November 2001, 10,000 pages were accessed per day. The media calls in the morning for traffic updates. There is a direct CCTV feed to the British Broadcasting Corporation. The operating and maintenance road agencies get their weather information from service providers and do not provide weather information on VMS.
Police have workstations for NADICS and can control everything in their "precinct," including signs and CCTV.
The CITRAC system is an on-line signal system that polls information every 24 seconds. It includes the BIAS - Bus Information and Signaling System, and archives the data for 6 years. A trial on real-time information for buses is currently being conducted. An automated parking guidance system exists for car park data. A license plate recognition system is used for journey time monitoring to provide travel times. It uses a specific route with cameras at both ends. The camera sites have loops next to them so they can also categorize (classify) cameras for different types of vehicles (one camera per lane).
The CITRAC system provides:
| << Previous | Contents | Next >> |